RADIOLOGY DEPARTMENT
Ultrasound
Philips Affinity 30
Ultrasound Scanning is a diagnostic imaging technique based on the application of ultrasound. It is used to see internal body structures such as internal organs, tendons, muscles, joints & blood vessels. Doppler ultrasound scan helps doctors assess the blood flow through major arteries and veins, such as those of the arms, legs, and neck.
- Test Performed
- Ultrasound carotid doppler
- Ultrasound chest
- Ultrasound color doppler av fistula
- Ultrasound color doppler both limb (arterial / venous)
- Ultrasound liver doppler
- Ultrasound peripheral doppler
- Ultrasound renal doppler
- Ultrasound color doppler pregnancy
- Ultrasound color doppler tvs
- Ultrasound obstetrics doppler
- Ultrasound breast
- Ultrasound early pregnancy
- Ultrasound early pregnancy (TVS)
- Ultrasound follicular study TVS
- Ultrasound growth scan (pregnancy)
- Ultrasound NT scan
- Ultrasound target scan
- Ultrasound target scan twins
- Ultrasound obstetric
- Ultrasound TVS
- Ultrasound pelvis + tvs
- Ultrasound pelvis+obstetric+tvs
- Ultrasound gluteal region
- Ultrasound b/l scrotal and inguinal area
- Ultrasound KUB
- Ultrasound KUB with PVR
- Ultrasound pelvic floor imaging
- Ultrasound pelvis
- Ultrasound Upper abdomen
- Ultrasound whole abdomen
- Ultrasound elbow
- Ultrasound small part (neck, thyroid, scrotum, ankle, knee, sternum nodule etc)
Computed Tomography (CT Scan)

Philips Access CT
A CT scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce images of the inside of the body. It shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, organs and blood vessels. CT scans may be performed to help diagnose tumors, investigate internal bleeding, or check for other internal injuries or damage.
- Test Performed
- CECT (Contrast Enhanced CT)
- CT Angio
- 3D CT Scan
- CT Brain
- CT Orbit
- CT PNS
- CT Face
- CT Mandible
- CT Neck
- CT Chest
- HRCT Chest
- CT Shoulder
- CT Elbow
- CT Hand
- CT Temporal Bone
- CT Long Bone
- CT Whole Spine
- CT KUB
- CT Dorsal Spine
- CT Wrist
- CT Urogram
- Ct Whole Abdomen
- CT Sacrum/Coccyx
- CT Sternum
- CT Pelvis
- CT HIP
- CT Knee
- CT Ankle
- CT Foot
- CT Calcaneum
- CT Brain Angio
- CT Carotid Angio
- CT Celiac Angio
- CT Mesenteric Angio
- CT Hepatic Angio
- CT Peripheral Angio both limbs
- CT Aortogram Angio
- CT Pulmonary Angio
Digital X-ray

Allengers
Digital radiography is a form of X-ray imaging, where digital X-ray sensors are used. X-rays use invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs on film or digital media. They are often used to help diagnosed fractured bones, look for injury, infection or tumor and to locate foreign objects in soft tissue.
- Test Performed
- X-ray Chest
- X-ray Pelvis
- X-ray Abdomen
- X-ray KUB
- Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP)
- Retrograde Urethrography (RGU).
- Micturating Cystourethrography (MCU)
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
- X-ray Skull
- X-ray Skull Mastoids Townes
- X-ray Styloid Process
- X-ray Face Nasal Bone
- X-ray Face Paranasal Sinuses
- X-ray Mandible
- X-ray TM Joint Open & Closed Mouth
- X-ray Nasopharynx
- X-ray Cervical Spine
- X-ray Cervico- Dorsal
- X-ray Dorsolumbar
- X-ray Dorsal Spine
- X-ray Lumbo-Sacral Spine
- X-ray Sacrum
- X-ray Spine Sacrum & Coccyx
- X-ray Clavicle
- X-ray Steno-Clavicular Joint
- X-ray Shoulder
- X-arm
- X-ray Forearm
- X-ray ELBOW
- X-ray Hand
- X-ray Wrist
- X-ray Fingers
- X-ray Hip
- X-ray Thigh
- X-ray Knee
- X-ray Patella
- X-ray Leg
- X-ray Ankle
- X-ray Foot
- X-ray Calcaneum
- X-ray Toes
DEXA SCAN

GE Prodigy
A DEXA scan is an imaging test that measures bone density (strength). DEXA scan results can provide helpful details about your risk for osteoporosis (bone loss) and fractures (bone breaks). This test can also measure your body composition, such as body fat and muscle mass.
- Test Performed
- Dexa scan Hip / Spine/ Wrist (Radius)
- Dexa scan full body
- Fat analysis / Body composition study
UROLOGY DEPARTMENT
Uroflowmetry
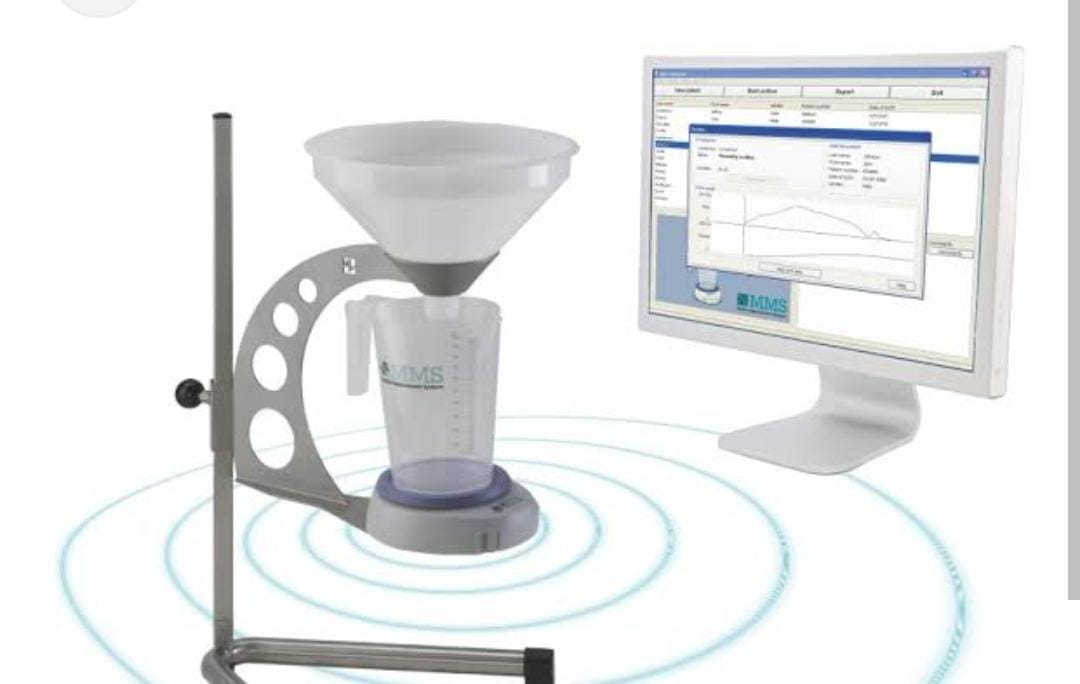

Uroflowmetry measures the flow of urine. It tracks how fast urine flows, how much flows out, and how long it takes. It’s a diagnostic test to assess how well the urinary tract functions.
- Test Performed
- Uroflowmetry
PULMONOLGY DEPARTMENT
PFT
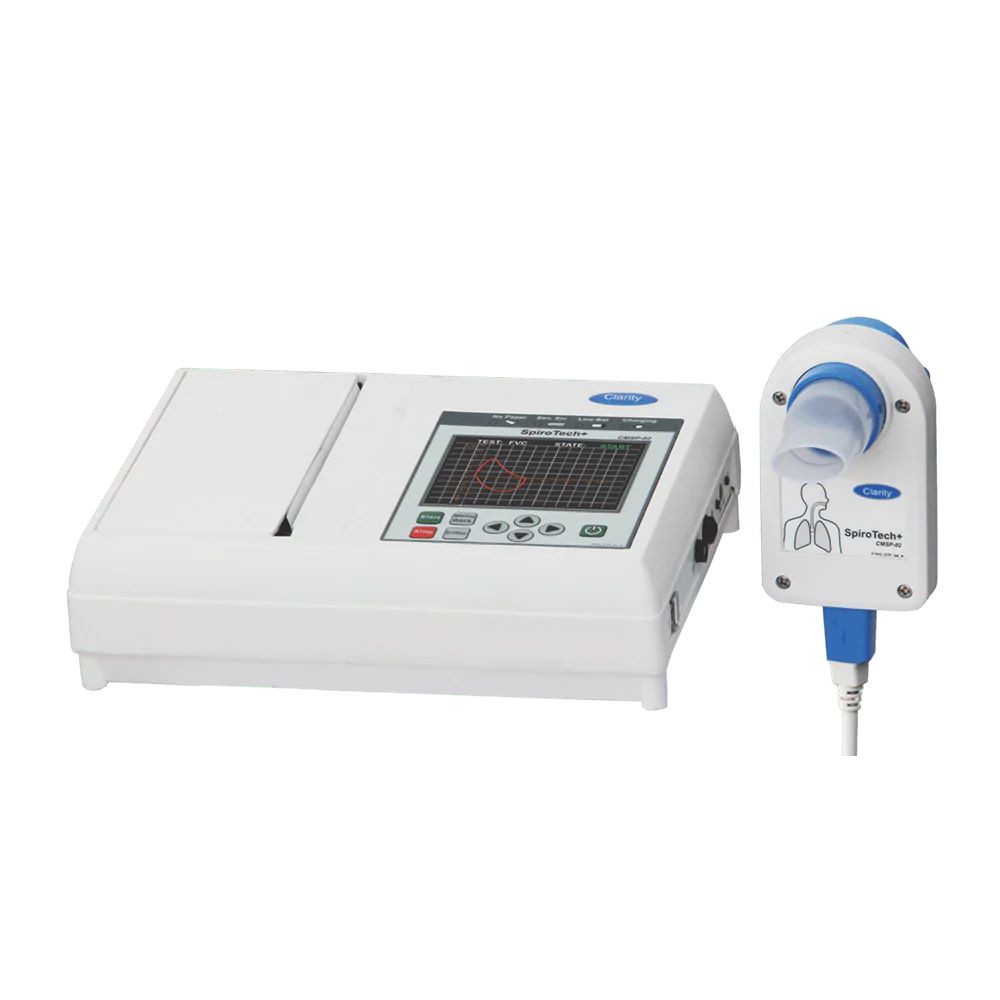

Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) are noninvasive tests that show how well the lungs are working. The tests measure lung volume, capacity, rates of flow, and gas exchange. This information can help your healthcare provider diagnose and decide the treatment of certain lung disorders.
- Test Performed
- Pulmonary Function Test (PFT)
CARDIOLOGY DEPARTMENT
Echocardiography (2D- Echo)
Philips Affinity 30
Echocardiography can be often referred to as Echo, ultrasound of the heart. The test produces essential information about the shape, size, location, pumping activities and other functions of the heart.
ECG
ECG is a test that helps to determine the heart functioning by checking the electrical activity of the heart. ECG is a painless test which measures the electrical signals generated from the heart.
Holter Monitoring
A Holter monitor is a small, wearable device that records the heart's rhythm. It's used to detect or determine the risk of irregular heartbeats.
NEUROLOGY DEPARTMENT
NEUROLOGY

Allengers
An EEG is a test that detects abnormalities in your brain waves, or in the electrical activity of your brain.
NCV is often used along with an EMG to tell the difference between a nerve disorder and a muscle disorder. NCV detects a problem with the nerve, whereas an EMG detects whether the muscle is working properly in response to the nerve's stimulus.
- Test Performed
- BERA
- Blink Reflex
- EEG Electroencephalogram
- EMG Electromyography
- NCV (NCS)
- Portable NCV
- RNST
- SSR
- VEP
- VIDEO EEG
SPECIAL TEST
Polysomnography/ Sleep study
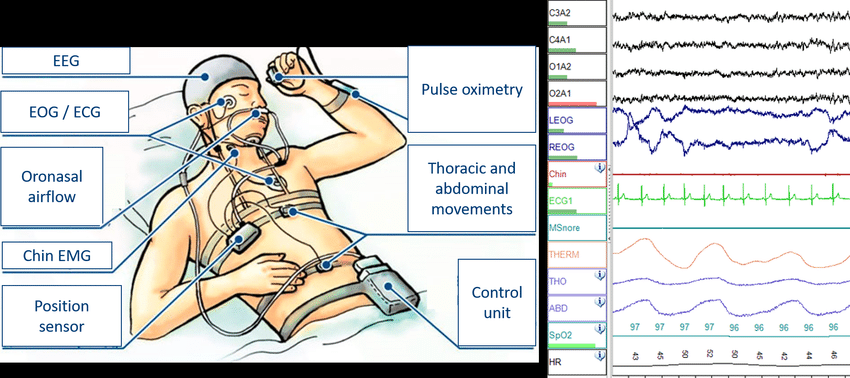
Polysomnography, also called a sleep study, is a comprehensive test used to diagnose sleep disorders. Polysomnography records your brain waves, the oxygen level in your blood, heart rate and breathing, as well as eye and leg movements during the study.Polysomnography may be done at a sleep disorders unit within a hospital or at a sleep center. In addition to helping diagnose sleep disorders, polysomnography may be used to help initiate or adjust your treatment plan if you've already been diagnosed with a sleep disorder.
- Type of Sleep Study
Level 1- A Level 1 Sleep study is used to help determine the cause of excessive daytime sleepiness and to diagnose various sleep disorders. A Level 1 study records your brain waves, heartbeats and breathing as you sleep. It also charts your eye movements, limb movements and oxygen in your blood.
Level 2 - A level 2 sleep study (also called Polysomnography) can also be completed from your own home. In addition to monitoring your breathing activity, oxygen levels, and heart rate, a level 2 sleep study monitors brain and muscle activity.
Level 3 - Level 3 sleep study is conducted in your home. The device provided records your oxygen levels, heart rate, airflow, snoring and other parameters while you are asleep.
Level 4 - A Level IV sleep testing device measuring three or more channels, one of which is airflow, is covered when used to aid the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in beneficiaries who have signs and symptoms indicative of OSA .



